Architecture
Program is stored in memory with 16-bit data bus. Data is stored in memory with 8-bit data bus. Both data buses are multiplexed. Therefore CPU can read lower bytes of program memory words.
CPU has the following registers:
- A,B,C,D - 8-bit general purpose registers
- M - (Memory) 8-bit register for memory access
- S - (Memory) 8-bit register for memory access
- L - (Link) 8-bit register for subroutines return address and memory access
- PC - 8-bit program counter
CPU has 3 flags:
- CY - carry
- Z - zero
- S - sign
Memory map
- 0x00 - 0x3f: program data
- 0x40 - 0x7f: reserved for program data
- 0x80 - 0x8f: two 8-bit input switches (first for even addresses and second for odd)
- 0x90 - 0x9f: teletype (input - keyboard, output - printing)
- 0xa0 - 0xff: unused (read as 0)
Instructions set
The computer has the following instructions’ classes:
- HALT
- NOP
- MOV
- LOAD
- STORE
- ALU operation
- CALL
- JUMP
- MOVI
All instructions have the same width of 16 bits.
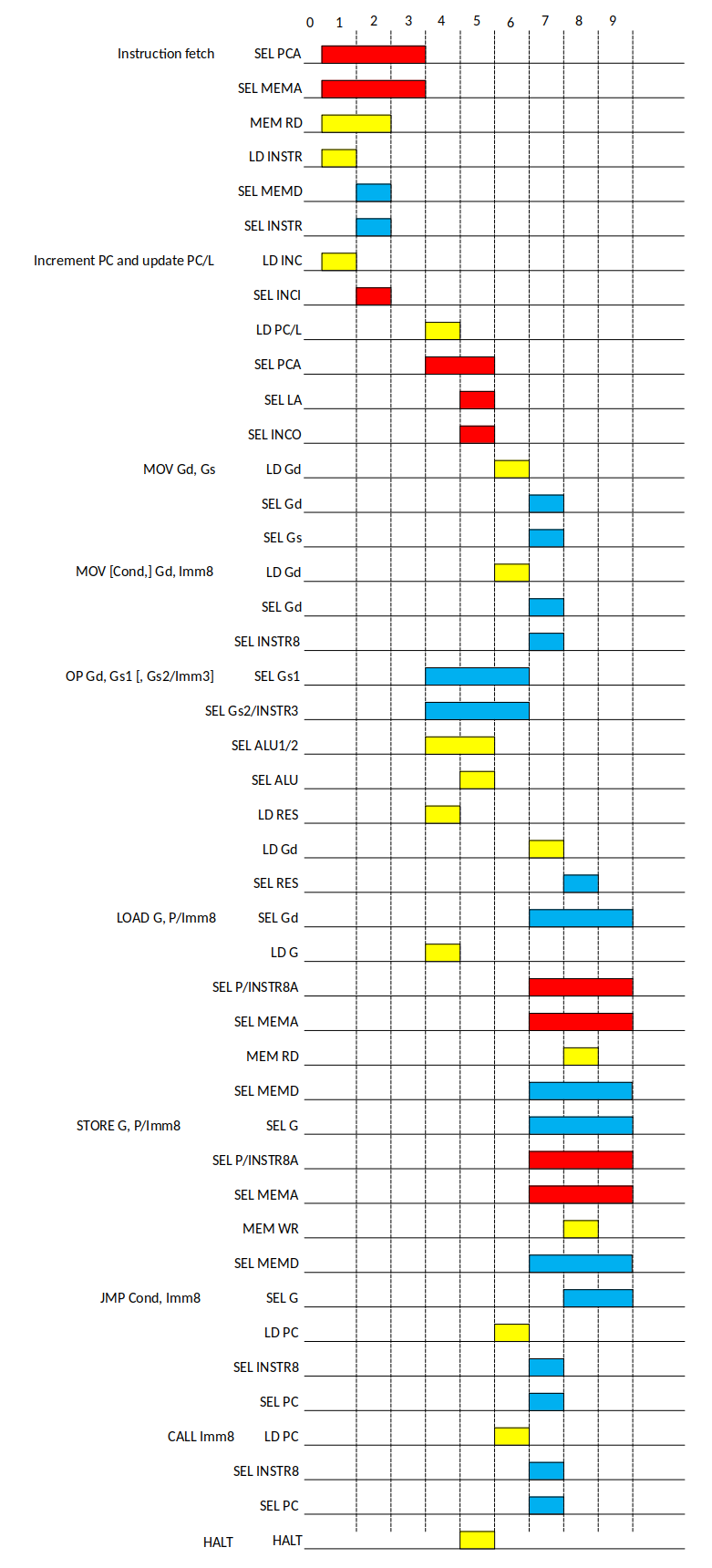
Instruction execution consists of the following phases:
- Fetch. During this phase instruction code is loaded from memory, and INC register is loaded with current PC value plus one.
- Update PC/L. INC value to PC or L depending of current instruction.
- Exec. Execute the instrucion and save the result to the destination.
ALU operations also performs loading of source values into it’s internal registers during the second phase of execution.
Instructions can have the following parameters:
- G - one of eight 8-bit registers (A, B, C, D, M, S, L, PC)
- P - one of 8-bit memory pointers (M, S, L, PC)
- Imm - immediate value (number of bits depends on instruction)
HALT
This class consists of a single instruction, which stops the clock and thus stops the execution of a program.
Intruction code:
00010--- --------
NOP
Does nothing.
Intruction code:
00000--- --------
LOAD
Loads single register from memory pointed by 8-bit pointer.
Format:
LOAD G, P
Instruction code:
00101ddd -----aaa
- a - code of address register P
- d - code of destination register G
Semantics:
G := Mem[P]
Result of reading of register through itself is undefined.
LOAD-Imm
Loads single register from memory pointed by 8-bit absolute address.
Format:
LOAD G, Imm
Instruction code:
00100ddd iiiiiiii
- i - immediate address
- d - code of destination register G
Semantics:
G := Mem[Imm]
STORE
Stores 8-bit register into memory at the address stored in 8-bit pointer.
Format:
STORE G, P
Instruction code:
00111sss -----aaa
- a - code of address register P
- s - code of source register G
Semantics:
Mem[P] := G
STORE-Imm
Stores 8-bit register into memory at the address specified in the instruction.
Format:
STORE G, Imm
Instruction code:
00110sss iiiiiiii
- i - immediate address
- s - code of source register G
Semantics:
Mem[Imm] := G
CALL
Calls subroutine specified with it’s address.
Format:
CALL [Cond,] Imm
There are the following possible conditions:
- 000: A / empty - jump always
- 001: Z - jump if zero (Z=1)
- 010: NS - jump if positive (S=0)
- 011: C - jump if carry (C=1)
- 100: NC - jump if not carry (C=0)
- 101: S - jump if negative (S=1)
- 110: NZ - jump if not zero (Z=0)
Instruction code:
1ccc1111 aaaaaaaa
- c - code of jump condition
- a - immediate value of subroutine address
Semantics:
if (cond) L := PC + 1
if (cond) P := Imm
JUMP
Performs conditional or unconditional jump to the specified address.
Format:
JMP [Cond,] Imm
There are the following possible conditions:
- 000: A / empty - jump always
- 001: Z - jump if zero (Z=1)
- 010: NS - jump if positive (S=0)
- 011: C - jump if carry (C=1)
- 100: NC - jump if not carry (C=0)
- 101: S - jump if negative (S=1)
- 110: NZ - jump if not zero (Z=0)
NC, NZ, and NS codes are inverted versions of C, Z, and S respectively.
Instruction code:
1ccc0111 aaaaaaaa
- c - code of jump condition
- a - immediate address
Semantics:
if (cond) P := Imm
Simplified mnemonic:
- JMP Imm - JMP A, Imm
MOVI
This instruction loads 8-bit immediate value into 8-bit register. There is a condition field which enables conditional execution of this instruction.
Format:
MOVI [Cond,] Gd, Imm8
Instruction code:
1ccc0ddd iiiiiiii
- c - condition
- d - code of Gd register
- i - immediate value Imm8
There are the following possible conditions:
- 000: A / empty - assign always
- 001: Z - assign if zero (Z=1)
- 010: NS - assign if positive (S=0)
- 011: C - assign if carry (C=1)
- 100: NC - assign if not carry (C=0)
- 101: S - assign if negative (S=1)
- 110: NZ - assign if not zero (Z=0)
NC, NZ, and NS codes are inverted versions of C, Z, and S respectively.
Semantics:
if (cond) Gd := Imm8
MOV
These instructions perform copying of one 8-bit register to another.
Format:
MOV Gd, Gs
Instruction code:
00011ddd -sss----
- d - code of Gd register
- s - code of Gs register
Semantics:
Gd := Gs
The result of assignment register to itself is undefined. When PC is read, then address of next instruction is read.
Simplified mnemonics:
- RET - MOV PC, L
Binary ALU operations
ALU can perform binary operations on any pair of 8-bit registers. The result of operation can be stored in eny 8-bit register.
Format:
OP Gd, Gs1, Op2
- OP - operation to calculate
- Gd - destination register, or F when the result is not saved
- Gs1 - first operand
- Op2 - second operand - register or 3-bit immediate value
Instruction code:
01bbbddd ixxxryyy
- b - code of operation
- d - code of destination register
- x - code of the first operand
- y - code of the second operand
- r - write back the result to the destination register
- i - immediate version
ALU supports the following binary operations that are encoded by ‘a’ field of the instruction code:
- ADC - calculates sum of operands and carry
- ADD - calculates sum of operands
- SBC - subtracts second operand and carry from the first one
- SUB - subtracts second operand from the first one
- AND - calculates bitwise AND
- OR - calculates bitwise OR
- XOR - calculates bitwise XOR
- Unary - performs unary operation instead of binary. See the next section for details
Semantics of the operations:
Op2 value for all operations:
if (i == 0)
Op2 = Reg[yyy]
else
Op2 = yyy
ADC (code 000):
Res = (Gs1 + Op2 + CY) & 0xff
CY = (Gs1 + Op2 + CY) >> 8
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
ADD (code 001):
Res = (Gs1 + Op2) & 0xff
CY = (Gs1 + Op2) >> 8
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
SBC (code 010):
Res = (Gs1 - Op2 - CY) & 0xff
CY = ((Gs1 - Op2 - CY) >> 8) & 0x1
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
SUB (code 011):
Res = (Gs1 - Op2) & 0xff
CY = ((Gs1 - Op2) >> 8) & 0x1
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
AND (code 100):
Res = Gs1 & Op2
CY = 0
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
OR (code 101):
Res = Gs1 | Op2
CY = 0
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
XOR (code 110):
Res = Gs1 ^ Op2
CY = 0
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
if (r)
Gd = Res
Simplified mnemonics:
- CMP Op1, Op2 - SUB F, Op1, Op2
- TST Op1, Op2 - AND F, Op1, Op2
Unary ALU operations
Unary operations can be performed on any of 8-bit registers. The result of operation can be stored in eny 8-bit register.
Format:
OP Gd, Gs
- OP - operation to calculate
- Gd - destination register, or F when the result is not saved
- Gs - operand (source) register
Instruction code:
01111ddd -sssruu0
- d - destination register code
- s - source register code
- u - code of operation to perform
- r - write back the result to the destination register
Unary operations are the following:
- NOT - bitwise not
- SHR - shift to right
- ROR - rotate to right
- RCR - rotate through CY to right
There are no shift left operations, because they can be simulated with ADD/ADC instructions.
Semantics of the operations:
NOT (code 00):
Res = ~Gs
CY = 0
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
ROR (code 01):
Res[0:6] = Gs[1:7]
Res[7] = Gs[0]
CY = 0
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
SHR (code 10):
Res[0:6] = Gs[1:7]
Res[7] = 0
CY = Gs[0]
Z = Res == 0
S = 0
RCR (code 11):
Res[0:6] = Gs[1:7]
Res[7] = CY
CY = Gs[0]
Z = Res == 0
S = Res >> 7
if (r)
Gd = Res
Instruction timings